News

12 October 2022
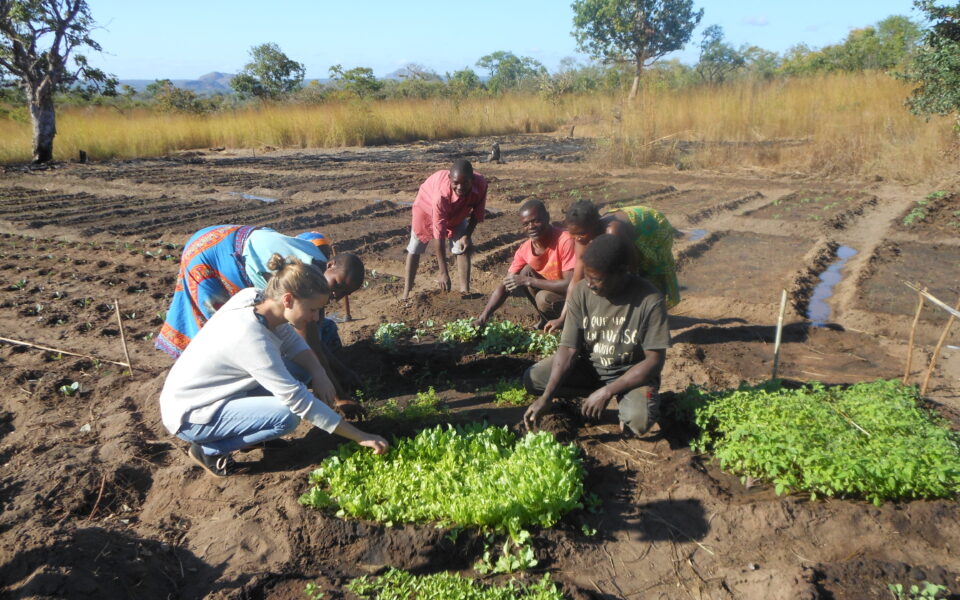
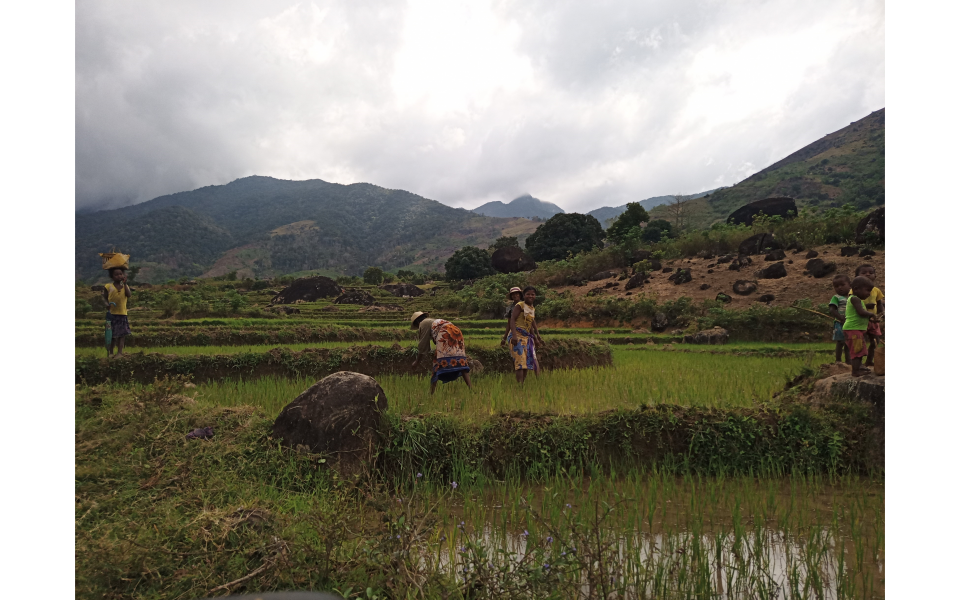
SalvaTerra has finalized the feasibility study of the Talaky Be project in the Anosy region
In a context already marked by extreme poverty, high food insecurity and high deforestation rates, the effects of climate change are impacting and will impact already very vulnerable rural households.
As part of the AdaptAction facility, AFD and the Government of Madagascar called on SalvaTerra to pilot the feasibility study of a large-scale territorial project. This “Talaky Be” project should contribute to improving the living conditions, food security and resilience of rural populations to the effects of CC, through the dissemination of sustainable and climate-smart agriculture as part of integrated territorial management and sustainable restoration of landscapes and forests in the Anosy region.
It benefits from the long experience of AFD and its partners in the region, including the Talaky project (2018-2022), and before it the Holistic Forest Conservation Program (PHCF, 2008-2013 and 2013-2018). These projects, operated by Nitidae and Agrisud International, aimed in particular at the conservation of natural ecosystems and the improvement of the living conditions of rural populations in the Beampingaratsy corridor, in the Anosy region.
With its partners BEST, EGIS, IRD and Carbonium, SalvaTerra produced 10 deliverables including the complete technical and budgetary feasibility study of the Project.
A lire aussi...

20 Feb. 2026
Mission à Béjaïa : vers un système intégré d’alerte précoce et de réponse rapide aux feux de forêt
Dans le cadre de notre appui à la Wilaya de Béjaïa, une mission de terrain s’est tenue entre Alger et Béjaïa afin de poser les bases d’un dispositif structuré de prévention, d’alerte et d’intervention face au risque incendie.
19 Feb. 2026
On parle de nos travaux dans le cadre du projet Giroflee – Gestion Innovante des Ressources Forestières pour une Energie durable dans la presse réunionnaise !
"Cette rencontre a marqué une étape à mi-parcours avec la présentation des résultats intermédiaires du projet, notamment la restitution finale de l’étude stratégique des acteurs et des flux de la filière forêt-bois réunionnaise réalisée par le bureau d’étude SalvaTerra. Cette étude a permis d’établir une vision consolidée de la filière en cartographiant ses acteurs, en analysant les flux existants et en identifiant les principaux leviers et enjeux économiques, techniques et organisationnels du territoire (...)".
